The Definitive Guide To SEO In 2023
This is the ultimate guide to search engine optimization in 2023. It’s something I’ve been passionate about for 14+ years now – so I know what works and what doesn’t.
If you want to spend your time and effort focusing on what works versus what doesn’t, keep on reading.
This is NOT your average “SEO in 2023” predictions post. In fact, it’s NOT that all – quite the opposite actually.
Yeah, I’m going to cover the most important SEO trends and what SEO ranking factors are the most important.
However, you’re also going to see new strategies that are working great right now.
So if you’re looking to improve your SEO in 2023, you’ll love this updated guide we have for you.

Table Of Contents

Chapter 1: Core Web Vitals
In this chapter, we'll be discussing Google's 2021 Core Web Vitals update.

Chapter 2: Google Passages
In this chapter, we'll be discussing the important Google Passages update.

Chapter 3: Featured Snippets
In this chapter, we discuss what you need to know about Featured Snippets.

Chapter 4: Authority And Expertise
In this chapter, we'll cover the vital
E-A-T updates from Google.

Chapter 5: Visual Search Trends
In this chapter, we'll be covering visual search trends to watch in 2022.

Chapter 6: Video SEO
In this chapter, you'll learn how to optimize video for SEO.

Chapter 7: Mastering Search Intent
In this chapter, we break down how to master search intent in your SEO.

Chapter 8: Local SEO
In this chapter, you'll learn everything you need to know about local SEO.

Chapter 9: SEO Content
In this chapter, we share a few SEO secrets to rank content high in Google.
Chapter 1:
Core Web Vitals
This came down from Google itself, the core web vitals update became a ranking factor in 2021.
From what I’ve seen since the full release, this has become a very important SEO ranking factor. In this chapter, I’m going to show you exactly how to get your site optimized for this new Google update.
If you haven’t focused on Core Web Vitals yet, don’t hesitate another second. I’m going to also share how I improved TeachingOnlineBusiness.com core web vital scores.)
Let’s get started.
Core Web Vitals: Here's Everything You Need To Know
Core web vitals are a set of three specific web page experience metrics that Google considers super important:
- Largest contentful paint
- First input delay
- Cumulative layout shift
According to Google, core web vitals will directly impact rankings.
While that is true, they also let us know that core web vitals are not a make or break ranking factor. In short, you can still rank well with poor core web vitals scores.
Still, these do have ranking factor influence over your SEO and they have UX implications. Due to this, you should take the time to optimize your site’s core web vitals.
It may feel overwhelming but it’s pretty straight forward.
Here’s how you can improve your CWV scores.
How To Improve Your Core Web Vitals Scores
There’s not a one size fits all approach to core web vitals.
The exact steps you’ll need to take to improve your core web vitals will vary on a wide range of different factors.
The best example I can think of – take (2) of the most popular apps to build a website on: WordPress and Shopify. If you run a WP site versus a Shopify site, you’re going to see completely different results, as well as contributing factors.
Even so, there’s a specific process you can use to figure out what you need to fix.
First things first, you’re going to need to open up Google Search Console and then click on “Core Web Vitals”.
Once you click on Core Web Vitals, you’ll be able to see ehere your site stands on Mobile and Desktop.
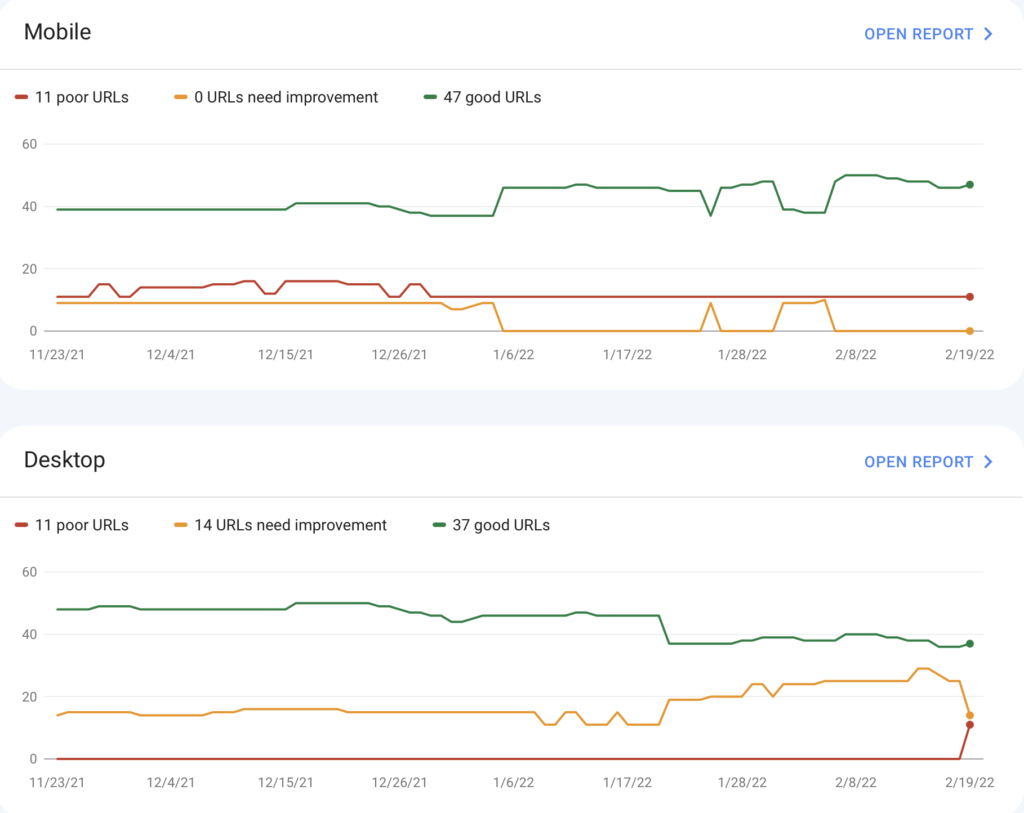
SEOs have mixed feelings on this. Some people will tell you to only focus on mobile, others believe you should do both desktop and mobile (I’m one of those). There’s no question that Google puts a larger importance on mobile – Google’s mobile-first index means that mobile scores should be your main focus.
Even so, I’d still recommend optimizing desktop URLs too.
For some industries, desktop may be the preferred method for “choice of device.”
The end goal should be aiming for no poor URLs.

We already know it’s not a big SEO ranking factor as of now, it could change in the future but not right this minute.
Due to this, if you have a lot of poor ranking URLs, Google is likely giving you a slap on the wrist for that performance versus good URLs helping you rank higher in Google. I may be wrong, but that’s what I’m seeing across the board on client sites.
It doesn’t matter if I’m correct or not, you still need to prioritize the poor URLs and get them fixed, turning red URLs to green or yellow.
What you do to start fixing them is going to depend on the core web vital areas you’re struggling in.
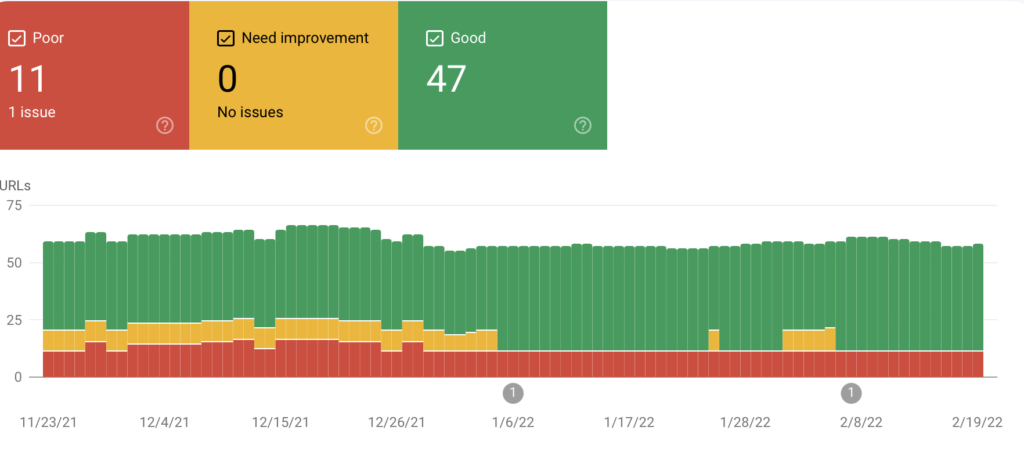
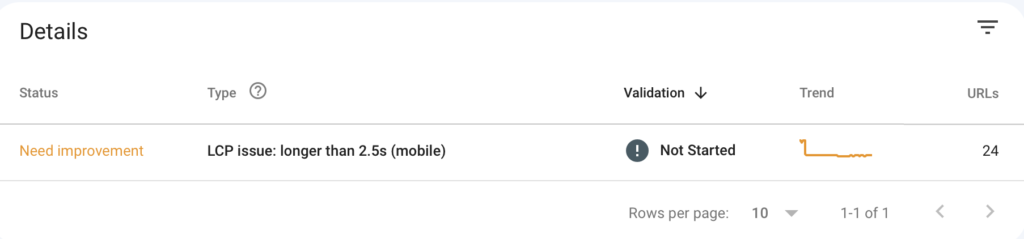
In my example, I have 11 pages with a LCP issue.
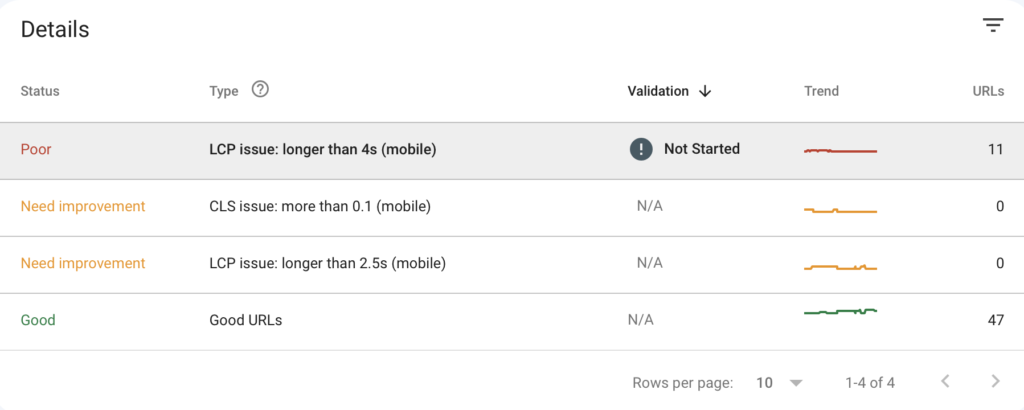
Our agency team has fixed a wide range of Core Web Vital issues that come up with our clients.
We had a client that had a 4.8s LCP on mobile.
We were able to help them get that down to the 2.5s range, which allowed us to get out of the red poor area.
How To Improve Your Core Web Vitals
When Google announced their upcoming page experience update, I realized that we needed to make a change.
The client’s load speeds were slow. Remember, we had a LCP issue. Let me explain what that means.
LCP stands for Largest Contentful Paint. LCP measures the time taken by the server to display the largest visible element in the viewport.
LCP should be less than 2.5 seconds. If you are seeing the LCP issue: Longer than 4s (Desktop) or (Mobile) error in your Search Console then it means that the server is taking more than 4 seconds to render the largest visible element in the viewport.
Using Google Pagespeed Insights
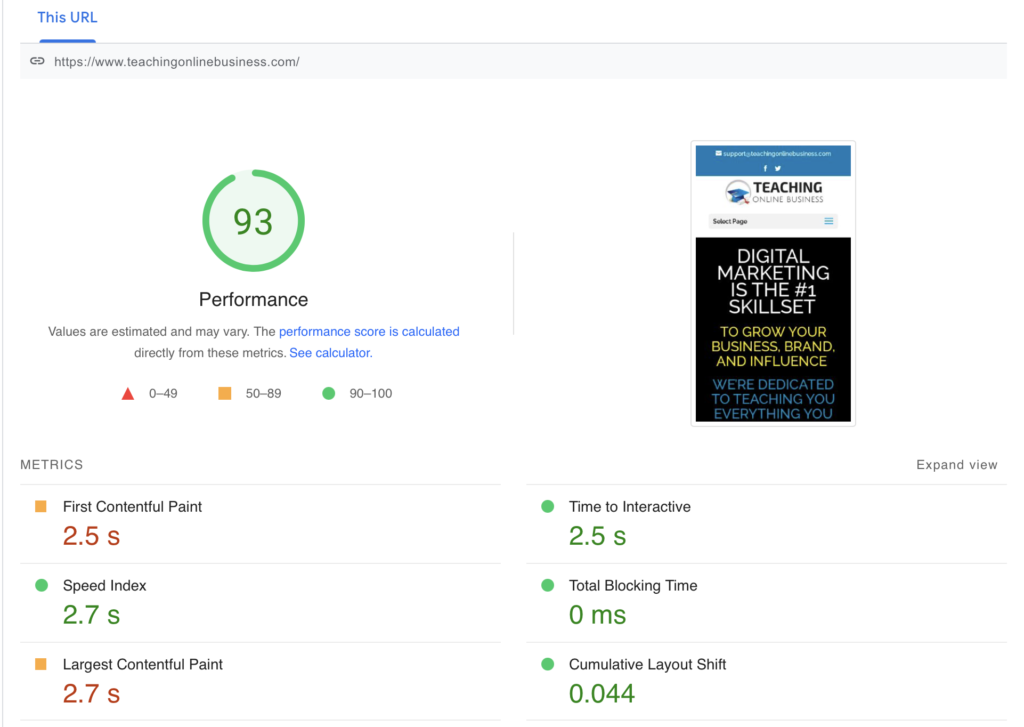
Once you have identified an example URL, visit Google Page Speed Insights and enter the URL of your page.
Please note: Enter the exact example URL in the tool and not your home page URL.
After the test is complete, you will see the LCP of your page. The LCP score is different for mobile and desktop. You only need to take care of the mobile score because fixing the mobile LCP will automatically fix the desktop or mobile LCP.
Once you’ve ran the Google Pagespeed test, you’ll see a section called OPPORTUNITIES.
This is where you’ll find Google’s recommendations to fix each pagespeed issue you have, including LCP, FCP, Speed Index, Blocking Time, Time to Interactive, and Cumulative Layout Shift.
In our case, the issue was on the server side. In other cases, it could be a layout or a specific element on your website.
You’ll be able to fix them all, but you may need a web developer if you’re not familiar with coding.
Chapter 2:
Google Passages
In 2020 Google announced a new search technology called “Passages”. This feature would allow Google to rank specific sections of a page, hence the name “a passage”). Reports say this feature is going to affect 7% of all searches. While that may not sound like a lot, this is a BIG number.
To give you some context here, Google Penguin only impacts around 3.1% of all queries. Google Passages is very important and will impact search results for years to come.
I’m going to teach you how to optimize your pages for this new Google ranking factor.
Here’s how you do it.
What Is Google Passages?
Google passage indexing is an automated feature that pulls sections from pages into search engine results, even if the page covers a slightly different topic from the main one.
Let me share an example with you. We’ll say you wrote a long-form post about digital marketing. Your goal was to cover the topic in its entirety, so you included sections on how to be a successful digital marketer, what digital marketing tools to use, what digital marketing networks are most popular, and how to get started in affiliate marketing.
That is a ton of useful content, but it also means your entire post probably won’t rank well for terms like “digital marketing networks” because only one section covers that topic.
With passage indexing, Google can pull out sections of your content and rank it independently of the rest of the page. For example, your section on “digital marketing tools” might rank for that keyword, even if the entire post isn’t optimized around that one specific keyword.

In the example above, notice how Google is using bold for certain words it deems relevant to the search. It’s looking for keywords that show the content is likely to be useful for a specific search query.
Google’s Martin Splitt said he would label the changes “Passage Ranking” because it’s actually a ranking change rather than an indexing change, so you be the judge of how the terms are being used. Passage Ranking, Passage Indexing, you now know what they both mean.
How Does Google Passages Work?
Passages allow Google to rank specific, relevant passages from a specific page, these passages are what you know to be “sections.” Just like this article you’re reading, it has clear defined sections. I did this on the purpose. Before this specific update, Google always ranked the page as a whole, they wouldn’t take individual sections into account.
Not anymore, instead of Google ONLY taking into account the relevancy of an entire page, they now have the ability to evaluate the relevancy of a specific section of that page for ranking purposes.
Despite the updates, Google has been clear that they will still account for the whole page. All of your on-page and on-site SEO ranking factors are still going to have influence here, backlinks, UX, engagement, on-page SEO, and Google’s other page-level SEO factors will still play a role in rankings.
When all is said and done, this means a single page now has a higher opportunity to rank.
How Do You Optimize For Google Passages?
When it comes to appropriate SEO optimizations for Google Passages, it’s pretty straightforward – you need to organize your content into individual sections, just like this article here. This is the perfect example of how you can optimize your content for the Google Passages Update.
In simple terms, you want to dividie your content up into dedicated sections.
Each section of your content should cover a specific subtopic or subheading. That piece of content should go into depth about the topic being discussed.
If you are already creating content like this, you don’t have to change anything. In fact, you may have already noticed an increase in your overall SEO, especially your rich content rankings.
If you’re not creating content like this, I’d recommend starting right away.
You can also go back and re-optimize your older content, ensuring each article has clear sections moving forward.
Optimize Your Article Sections With Chapters
As you can once again see in this article, I’m using chapters to seperate each section of content on the page.
Each section serves as a H2 – although we’re also using H3 in other articles as we’re exploring to see which produces the best results.
If you’ve been following me for some time, you know how I feel about long-form SEO content.I’m a big advocate for it because there’s not many negatives I can find.
The one negative I bring up is the fact that Google can rank thin content over long-form content. Many of you have likely seen the same. The good news – I feel this is changing now.
Since Google Passages was released in 2020, I’ve continued to tell my students and clients to focus on long-form content. Out of 50 cases I monitored, 49 our of 50 websites saw an increase in organic ranking keywords and ranking positions.
If you didn’t know, Google can parse a single piece of long-form content into 5, 10, 20, 50, even 100 unique passages within an article. That is huge for those of us that has always believed in long-from content being the core control for SEO.
With the Google Passages Update, optimized individual sections now have a solid opportunity of ranking in Google.
Even better, this gives long-form content a competitive edge as it pertains to ranking higher in Google.
That has changed, instead of Google ONLY taking into account the relevancy of an entire page, they now can evaluate the relevancy of a specific section of that page for ranking purposes.
Now, Google has been very clear that they will still account for the entire page. All of your on-page and on-site SEO ranking factors will apply here, backlinks, UX, engagement, on-page SEO, and Google’s other page-level factors still matter.
When you break it all down, this means a single page now has a higher opportunity to rank.
Google and SEO moves in trends. This clearly shows long-form SEO content is a greater control now than any other period of time. It’s a big win for the SEOs that use it as a base foundational piece.
Chapter 3:
What Is Featured Snippets And How To Optimize For Them
Featured Snippets are prime Google real estate.
According to SEMrush, 6.2% of all search results have a Featured Snippet.
And yes: Featured Snippets are stealing A LOT of clicks from the #1 spot.
(As I like to say: “#0 is the new #1”.)
The question is: How do you get your content to appear in the Featured Snippet?
Here’s the process I use myself.
Find Your Featured Snippet Opportunities
6.2% may not sound like a lot, but this is a lot of searches that has featured snippet. Considering Google has billions of search results, that adds up to a lot of opportunities to get your website listed at the top of Google.
Just like you are now, a little research can go a long way, here’s what you need to know.
Step One: Keyword Research
The 1st step is going to be keyword research. To begin, start reviewing keywords you already rank in Google, pay close attention to the search terms you rank best. Why? According to Ahrefs – 99.58% of all Featured Snippets are from pages that rank on the first page for that term.
Due to this, if you don’t already rank in the top 10, you have zero chance of ranking in the Featured Snippet spot.
Step Two: Featured Snippet Opportunities
How do you find Featured Snippet Opportunities?
While you can check for them manually, it’s far better to use SEO software or tools to help. I use Ahrefs and their “Organic Keywords” report.
It shows you keywords that you rank for… that also have a Featured Snippet:
Step Three: Optimizing Snippets
When you’re optimizing your pages for snippet opportunities, you’ll want to focus on a 40-60 word content block.
SEMrush did an study on nearly 7 million Featured Snippets. They found the most Featured Snippets are 40-60 words long, im my experiences, I’d agree with that 100 percent.
Step Four: Formatting Google Snippets
Next, you’re going to need to make sure your target featured snippets are formatted correctly.
As you can see in the image below, this is how Google formats them.

Chapter 4:
Google Authority And Expertise
For the better part of the last decade, Domain Authority focused around link building and backlinks.
Here in 2023, things have changed a lot, and you don’t want to get left behind.
Today, Google now evaluates your site based on Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness.
This term has been coined as E-A-T – and it was the standard for a few years. In December 2022, it changed. E-E-A-T stands for “Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness.” Until a Google update in December 2022, it was just E-A-T (no “Experience”).
In more ways than one, E-E-A-T is the new Domain Authority. While that’s true, backlinks are not dead. In fact, backlinks still carry a lot of SEO weight. However, you’ll need a different approach if you want to rank high in Google in 2023.
And in this chapter, I’ll cover everything you need to know about this important SEO trend.

Get Familiar With E-E-A-T
The most recent set of Google Quality Rater Guidelines REALLY focused on E-E-A-T.
Now, before we dive deep, please allow me to clarify.
E-E-A-T is not new. It has been a part of the guidelines for years.
What has changed is the fact that E-E-A-T is now a higher valued SEO ranking factor.
This is all points to Google and how they want to present results to the end user. Check it out, Google’s new “How Search Works” report mentions that they want to rank “reliable sources”.
It hasn’t always been this way, at least not to the level we have now. It’s become so important, Google even cited E-E-A-T as a key ranking signal. Say it again. Google cited E-E-A-T as a key ranking signal.
Now, how can you begin to improve your site’s E-E-A-T. You can do it in 4 simple to follow steps.
Step One: Be An Expert
If you’re an expertise in your field, you’re going to love this step. If you outsource your content, you could be in trouble.
Google wants to feature content that’s written by legit experts in their respected fields.
When you get reading this, there’s a clear message from Google. For example, they stated that medical content needs to be written by health care professionals. That’s pretty straightforward – Google wants real experts.
Expertise is tough to fake.
If you want your content to rank in 2023, it needs to be written by people that know their stuff.
(This is especially true in the health niche.)
Step Two: Experience
Experience matters, Google wants to show search results that are created by experienced experts.
Google must determine whether authors have topical expertise. Do they have the knowledge, qualifications, and credentials required to give reliable information?
You will see expertise and experience relate a lot, but the two do differ enough for Google to add it to the old E-A-T algorithm protocol.
Step Three: Always Be Transparent
I’d say it’s very likely that Google focuses on off-site signals to figure out your site’s E-A-T.
I’d say that’s a given.
When you dive deep into the rater guidelines – they spend a lot of time evaluating the site itself.
This likely involves:
- In-depth about page
- Easy to find contact page
- References and external links to sources
- Privacy policy and terms of service
- Author blocks on every article
In short, you want to make sure you’re being transparent across the board.
Step Three: Citations
The majority of Google’s evaluation of E-A-T focuses not on your website, but off your website.
In the grand scale of things, when you an expert, others will mention you. Your personal or brand signals should grow in due time.
Anyone can claim to be an expert, right? Get a website and you can more less write about what you want.
Now, getting other websites to agree with you, that’s a much harder element.
Google’s guidelines state that: “When the websites says one thing about itself, but reputable external sources disagree with what that website says, trust the external sources.”
That’s all you need to know my friend.
Besides creating an awesome site, how do you get other people to mention you and your site as a go-to resource?
First, you need to be cited on lots of other trusted websites.
While linked mentions are great, they’re not required. Google is smart enough to know if others are mentioning your name, company, brand, organization, or website. You’re going to benefit the most if those cites are coming from domains that Google trust.
Next, your site as a whole needs to be associated with a specific topic.
Again, this comes down to off-site mentions. You’ll benefit the most here by getting mentions from other authorities in your respected field.
Chapter 5:
Visual Search Trends
Visual Search is not on a lot of radars at this time, it certainly isn’t a SEO focus point, not yet that is. But I want you to begin paying close attention to it.
It’s a big deal to be in this guide, if I mention it, it’s super important.
Google is always adapting and evolving, most SEOs know that by heart. Something is always changing and based on recent trends, visual search may be closer to taking off in 2023 than not.
Here’s what you need to know.
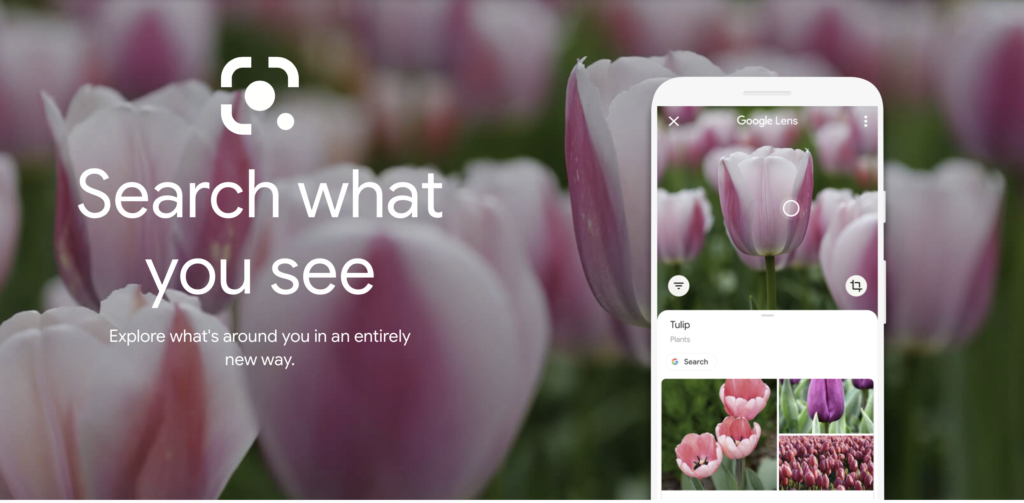
Visual Search Is Trending, So Pay Attention
With each passing year, more people are searching Google visually. Visual search is growing.
If you don’t believe me, just take a second to look at these metrics.
Google Lens has already been used 1 billion times (source).

You can do a lot of cool things with Google Lens.
I’ve been telling me friends and partners about it, I was shocked only a few of them knew about it.
With Google Lens, you can;
- Scan and translate text
- Take an image of anything, get images of that item back
- Copy and paste to your computer
- Identify animals and plants
- Help for homework
- And much more
Visual Search Technology
Visual search is very EARLY – we haven’t begun to see what it can become in the near future.
Even with the technology right now in 2022, it’s pretty awesome what can be done.
Take a few minutes to check it out here.
I’d recommend giving it a try on your mobile device. It doesn’t matter if you’re at home or work, on the road, start scanning items.
See? Yeah, pretty impressive. It can nearly identify anything and the tech is going to get better with time.
At the moment, Google Lens can identify 1 billion objects. And that number is growing every day.
Visual search is another big opportunity in SEO.
People Love To Search With Images
Once you get use to using visual search, you’re going to recommend it over other search features. I’ve quickly found it to be useful for:
- Shopping
- Checking out local areas
- Trying out different products
- Directions
- Identifying locations
- Local business reviews
- Translation
- Recipes
- Nutrition information
- And much more
Which is probably why 62% of young consumers want more visual search tech:
How To Optimize For Visual Search
A while ago we conducted one of the first visual search ranking factors studies.
Mobile Friendly Pages Matter: 9 out of 10 Google Lens results came from a site that passed Google’s mobile friendly test.
Image SEO Optimizations: Our research found that traditional image SEO techniques (like optimizing image filenames and alt text) seem to also help with Google Lens rankings.
And that high-authority pages and sites are more likely to appear as Google Lens results.
Long Form Content: We found that Google tends to pull Google Lens image results from pages with quite a bit of text (1600 words on average).
At first, this may seem surprising. But when you realize that Google specifically states that the text content on a page is important for image SEO, this finding makes a whole lot of sense.
Chapter 6:
Video SEO Optimizations
Online video is EXPLODING right now.
In fact, according to Cisco, online video will make up 82% of all online traffic by 2022.
82%!
And that may still not satisfy the world’s demand for video.
Despite the fact that there are more videos out there than ever, HubSpot states that 43% of people want even MORE video content.
In short:
If video isn’t part of your digital marketing plans, you’re missing out. Here’s how you can use video to improve your SEO this year.
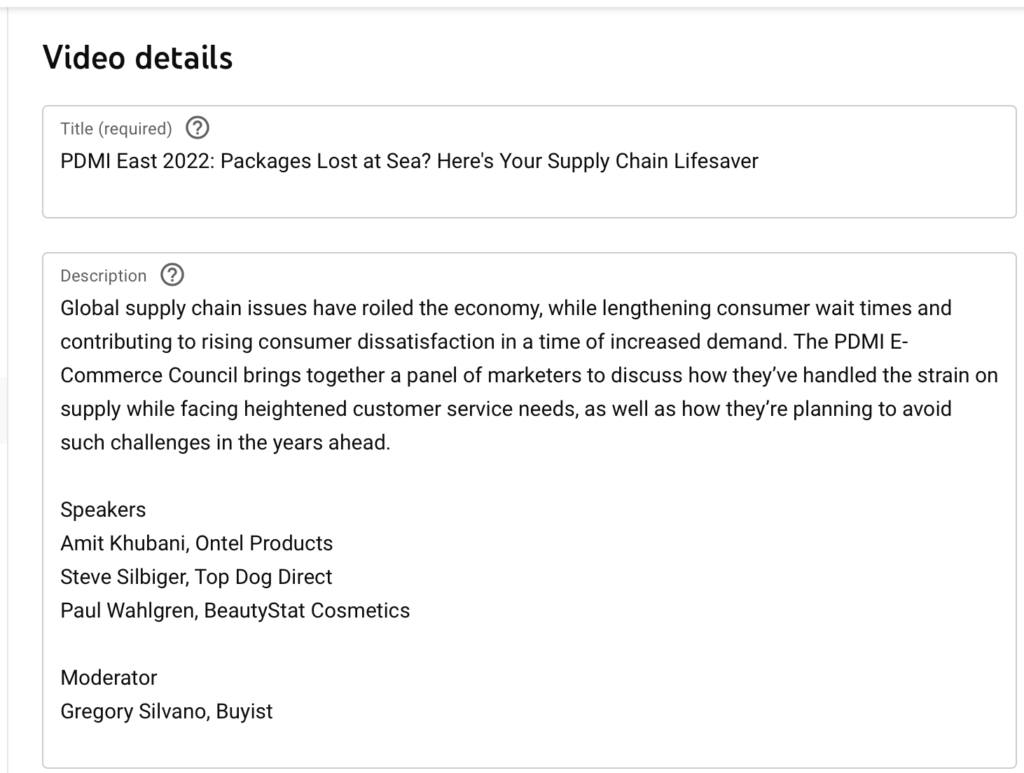
Video Featured Snippets And More Video Rankings
If you pay attention to search results or you use Google search a lot, you’ve likely noticed a lot more featured video snippets appearing versus anytime before.
In fact, Google highlighted Video Featured Snippets in their “Reintroduction to Featured Snippets” report.
And I expect to see more Video Featured Snippets in 2023.
From what I’ve seen, here are the 3 most important things to do to get your video content in a Featured Snippets.
(1) Make Sure Content In Videos Are Organized
This is extremely, extremely important.
You want to make sure your videos have clear sections, this is what helps Google understand the content in your video.
This also makes it easy for Google to use different clips from your video in video snippets.
(2) Optimize Videos With SEO
Google uses your title, description and tags to figure out what your video is all about.
You have a lot of real estate here to score some big SEO points.
So besides publishing videos that have clear sections, you also want to make sure that your video is optimized for SEO.
In fact, a small HubSpot study of 165 Video Featured Snippets found that 80% of them contained a keyword in the title.
(3) Make Sure You're Using Transcripts
The captions that YouTube automatically generates are REALLY good.
But it’s not 100%.
So to increase the odds that YouTube and Google can understand every word of your video, upload a transcript.
Grow Your YouTube Channel
YouTube is already the world’s 2nd largest search engine.
(In fact, according to a study by JumpShot and Moz founder Rand Fishkin, YouTube’s search engine is 2x more popular than Bing.)
Amazingly, YouTube is still growing.
In short, more and more people are searching for stuff on YouTube than ever before.
So if you want to get more traffic from SEO in 2022, I recommend creating and optimizing content specifically for YouTube.
It’s a search engine that’s too big to ignore.
The best part? Most marketers are too lazy to make videos. So it’s pretty easy to get your videos seen (assuming you know how to create high-quality videos).
For example, my channel has 45 total videos. And those 45 videos generate over 189k views per month.
(And as you might expect, a good chunk of those viewers turn into website visitors, leads and customers.)
It gets better: when you publish SEO-optimized YouTube videos, you’ll own more Google real estate.
Why? Well, for starters: 55% of all Google search results contain at least one video.
(And almost all of those videos are from YouTube.)
And considering that Google owns YouTube, expect even MORE YouTube videos in the search results in 2022.
Make Sure Your YouTube Videos Get Embeds
If people want to see more video content, why not give it to them?
That’s why I recommend embedding video content into your blog posts. And from my own Google Analytics data, I’ve seen that this can significantly improve your bounce rate.
Chapter 7:
Mastering Search Intent
Search Intent has been a massive topic in the SEO world over the last few years.
And for good reason:
Content that doesn’t match search intent simply won’t rank.
And as Google gets better at giving people the exact search results they want, creating content that’s a 1:1 Search Intent match is going to be a must for 2023 SEO.

Understanding Keyword Intent
Every keyword has an intent behind it.
Maybe it’s to look something up.
Or buy something.
Or compare product A with product B.
And the better your content can match that search intent, the better it will rank.
So your first step is to figure out your target keyword’s Search Intent.
Sometimes the intent is right in the keyword.
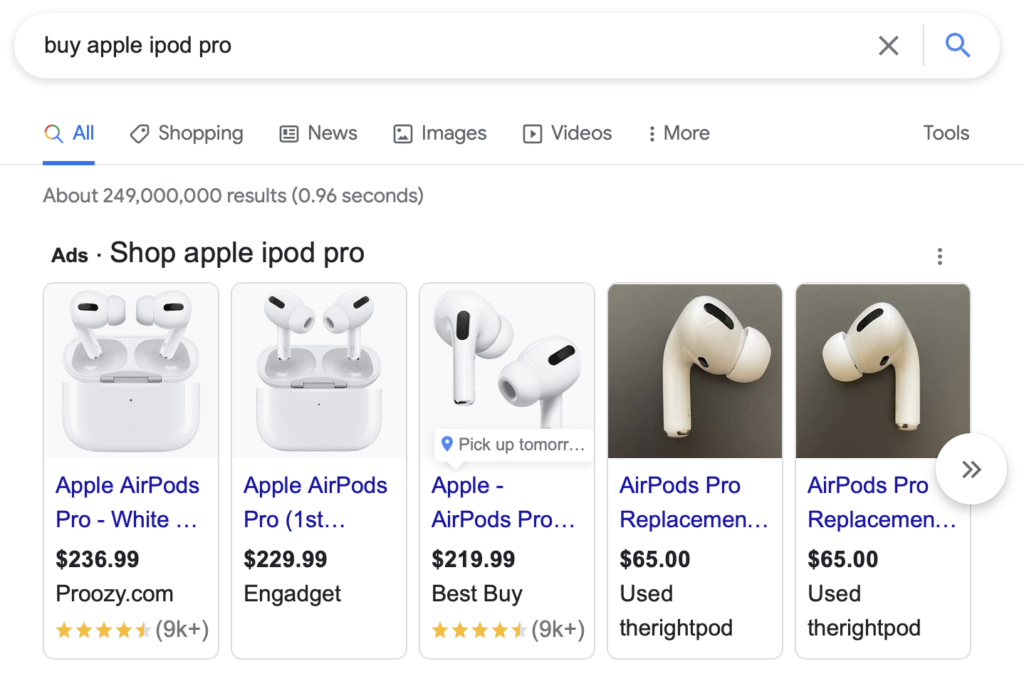
But it’s not usually that obvious. So for most keywords, the search results will tell you everything you need to know about that keyword’s Search Intent.
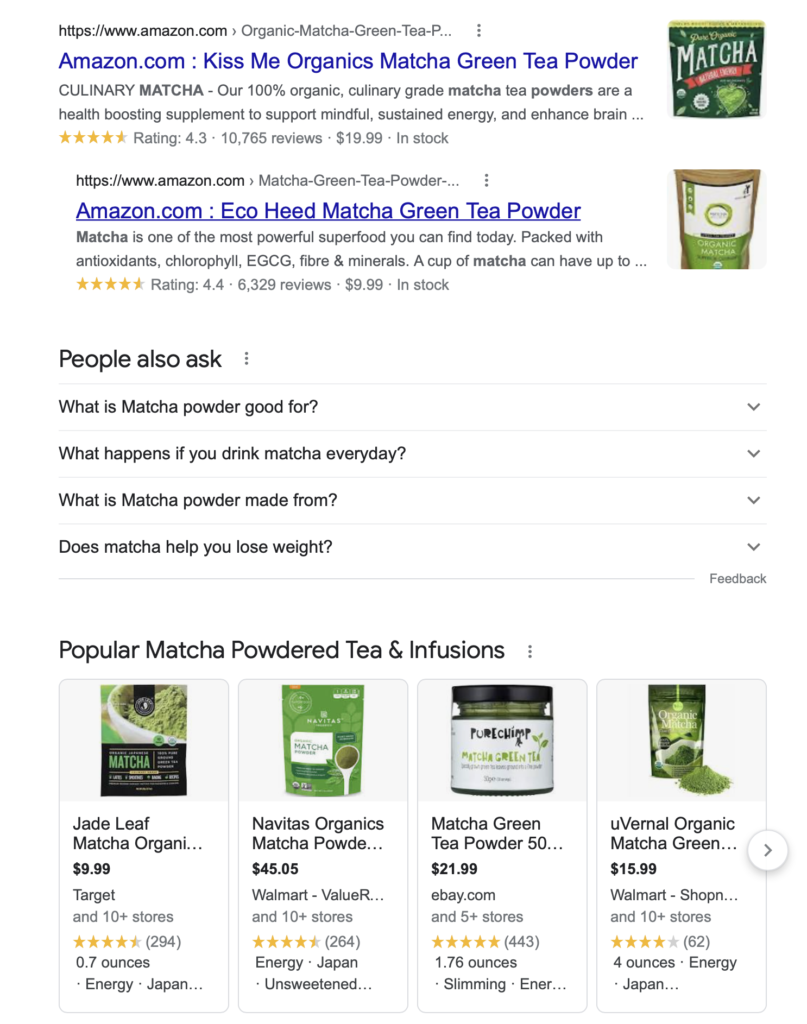
For example, take a keyword like: “protein powder”.
Someone searching for that term could want to buy some protein. Or maybe they want to learn more about it.
Well, according to Google’s first page for that keyword, most people searching for “matcha powder” are looking for products.
Create Content That Matches Search Intent
You need to evaluate every keyword you want to rank for and determine the Search Intent for each one of those keywords.
Once you’ve identified Search Intent, you can start creating content that gives searchers EXACTLY what they’re looking for. Simple.
Let me share an example, when I analyzed the search engine results pages (“the SERPs”) for “how to get YouTube subscribers”, I noticed that they were mostly list posts.
So even though this was a “how-to” keyword, I didn’t publish a step-by-step tutorial.
Instead, I published a list post.
Re-optimizing Old Content
If you haven’t been creating content focused around Search Intent optimization, you need to get started doing it now.
You should also start re-optimizing old content you have published.
Your older content likely has ranking potential, you can begin working on your older content to make it a better Search Intent fit to increase your on-site SEO, as well as improving the page’s overall user experience.
For example, this post used to rank really well for “SEO campaign”.
But as Google got better at figuring out what people that searched for that keyword actually wanted, my post started to drop in the rankings.
Which made sense: someone searching for “SEO campaign” doesn’t want a case study about a random guy. They want a list of steps.
So I transformed that post into a step-by-step guide that was easy to follow.
Chapter 8:
Local SEO
For the majority of this SEO guide, we’ve focused on how to rank your website generally.
If you run a local business, however, Google also lets you position it in front of potential customers in your area, specifically. But for that, you use local SEO.
And it’s well worth it.
46% of Google searches are for local businesses. They look for vendor suggestions, and even specific business addresses. In fact, 12% of customers look for local business information every day.
What’s more, they act on this information: 72% of searchers visit a local store or company’s premises within 24 hours of the search.
Google Business
The first thing you need to do for your local SEO is getting signed up with Google Business.
Google allows you to get verified, once you sign up for Google Business, they’ll send you a postcard that you’ll need to verify to get your business approved.
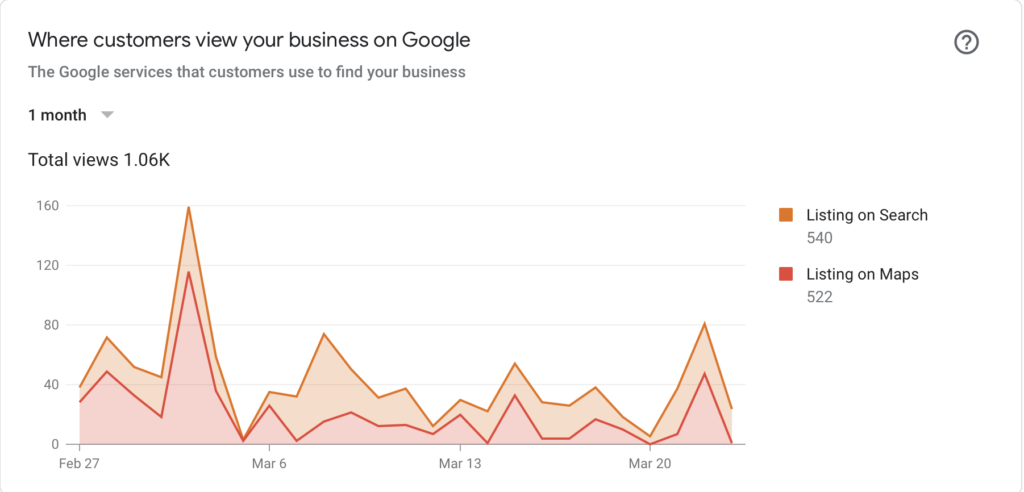
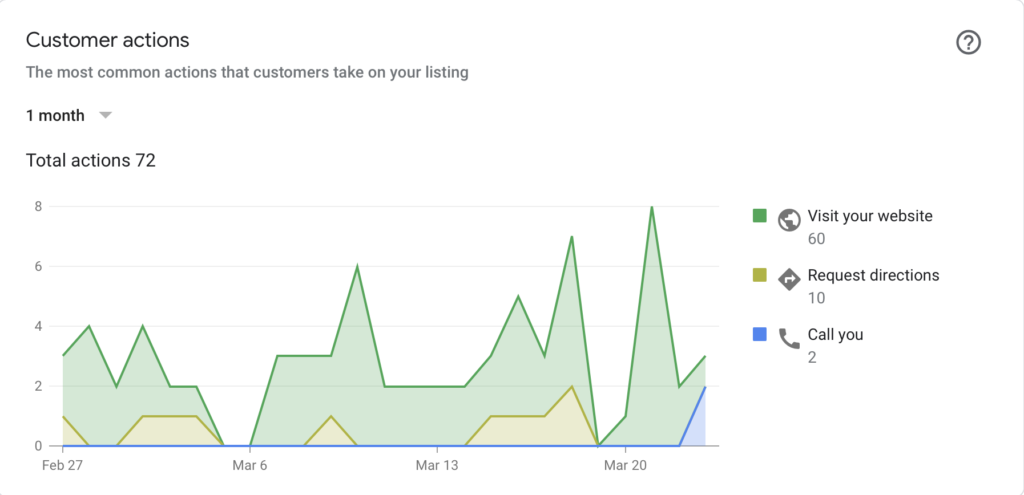
Inside your Google Business account, you can get insights for;
- Listings on search
- Listings on maps
- Website visits
- Direction request
- Phone calls
Google Business also allows you to submit your products and services, even allowing you to list descriptions for each.
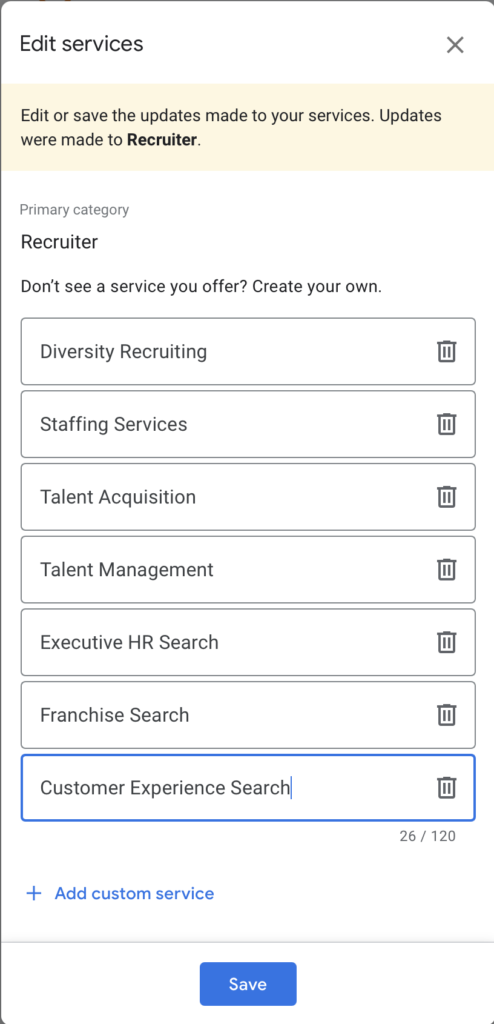
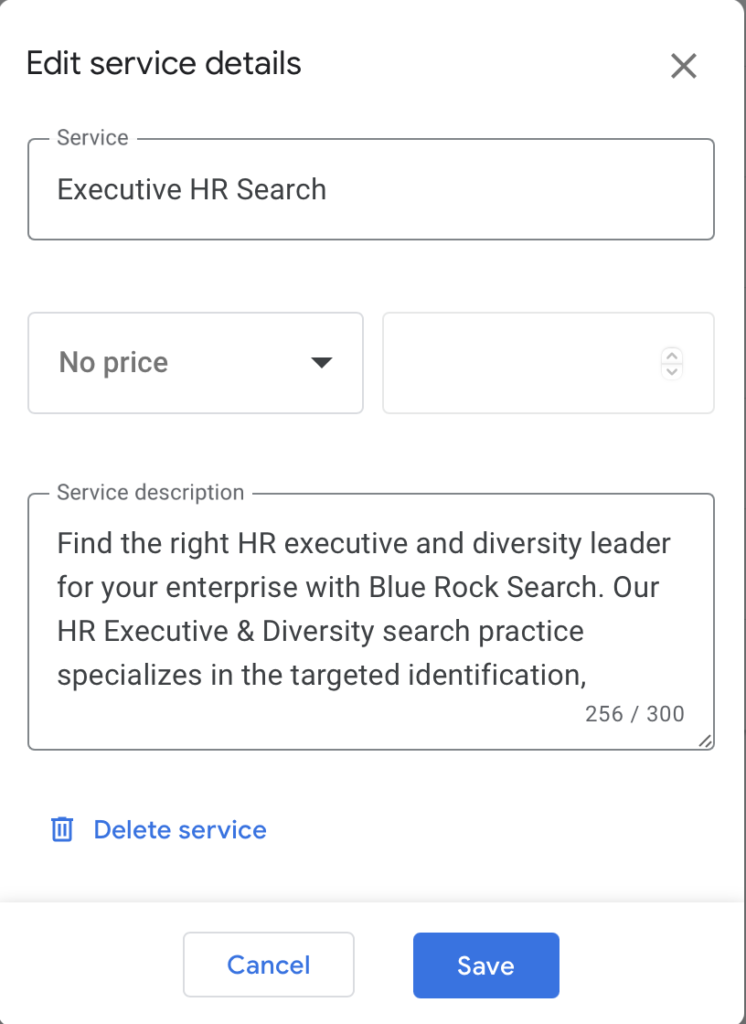
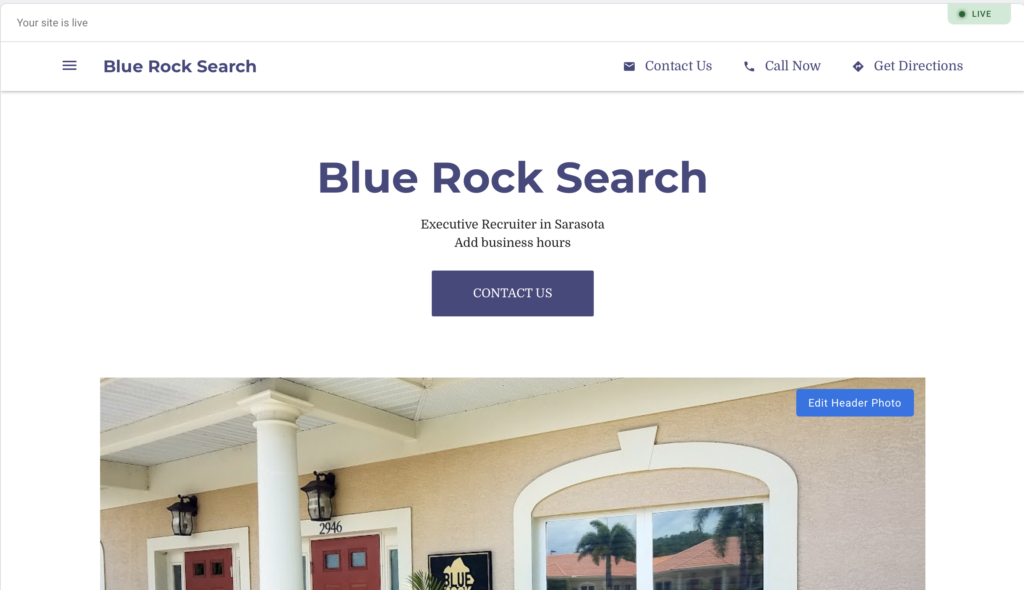
Google Business also allows you to publish a website that will use your business information to populate a one page website.
The site can have your images, reviews, and call-to-actions.
Local SEO Optimizations
Search engines follow similar principles for both local and global rankings. But given that they position a site for specific, location-based results, they need to analyze some other ranking factors too.
Even local search results look different:
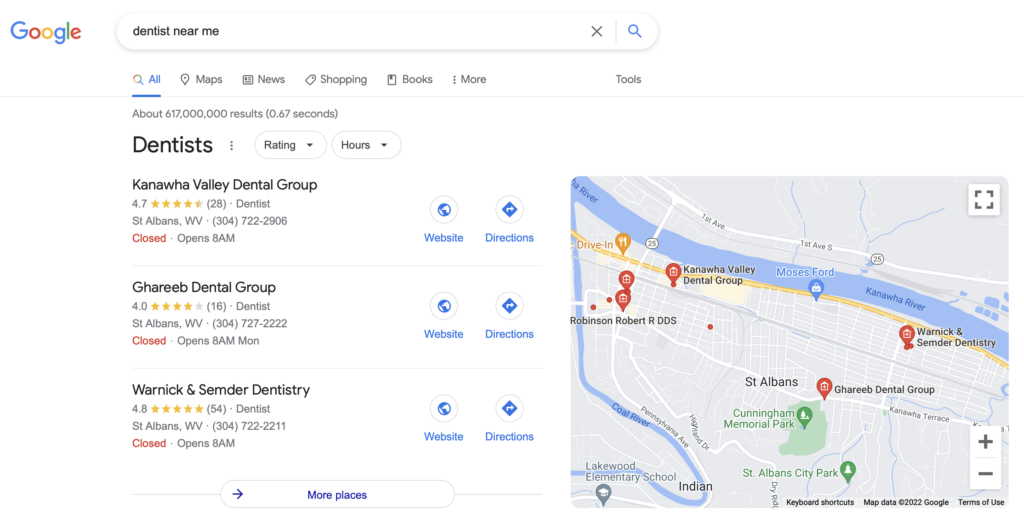
- They appear only for searches with a local intent (for example, “restaurant near me” or when a person clearly defined the location.)
- They contain results specific to a relevant location.
- They concentrate on delivering specific information to users that they don’t need to go anywhere else to find.
- They target smartphone users primarily as local searches occur more often on mobile devices.
For example, a localpack, the most prominent element of local results, includes almost all information a person would need to choose a business. Here are local results Google displays for the phrase “bakeries in Charleston.”
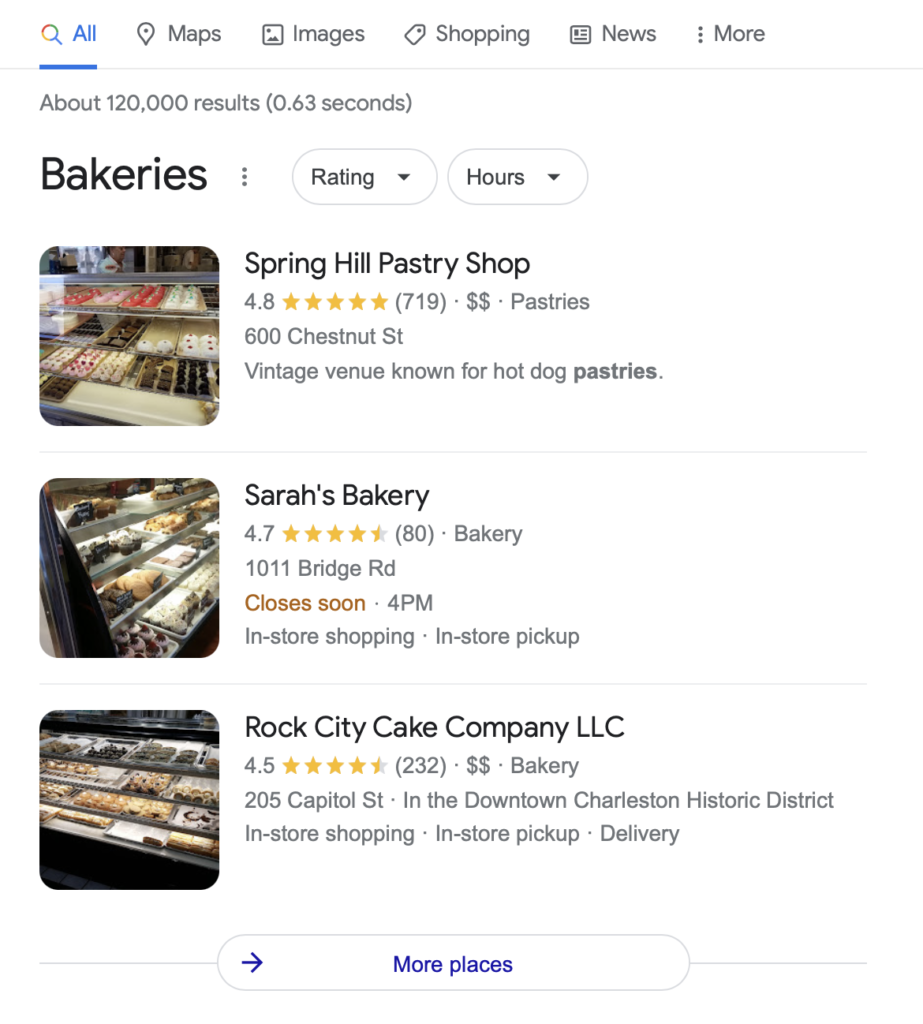
Note that these results contain no links to any content. Instead, they include a list of restaurants in the area, a map to show their locations, and additional information about each:
- Business name
- Description
- Image
- Opening hours
- Star Reviews
- Address
Often, they also include a company’s phone number or website address.
All this information combined helps customers choose which business to engage. But it also allows Google to determine how to rank it.
Local SEO Ranking Factors
When analyzing local websites, Google looks at the proximity to a searcher’s location. With the rise of local searches containing the phrase, “near me,” it’s only fair that Google will try to present the closest businesses first.
Keywords are essential for local SEO too. However, one additional element of on-page optimization is the presence of a company’s name, address, and phone number of a page. In local SEO, we refer to it as the NAP.
Again, it makes sense, as the search engine needs a way to assess the company’s location.
Google assesses authority in local search not just by links. Reviews and citations (references of a business’s address or a phone number online) highlight its authority too.
Finally, the information a business includes in Google My Business — the search engine’s platform for managing local business listings — plays a huge part in its rankings.
The above is just the tip of the iceberg. But they are the ones to get right first if you want your business to rank well in local search.
Chapter 9:
SEO Content
If you want to rank high in Google for 2023, you must create great content.
Google’s core SEO update in March 2023 proves this as they continue to enhance the value of on-site SEO content.
We’ve discussed the new Google Updated called Google Passages.
We’ve discussed why you need to know E-E-A-T, which stands for Expertise, Authority, and Trust.
You should focus on creating great SEO content, that is how you dominate SEO today.

How To Create Great SEO Content
With Google Passages and E-E-A-T updates, you’re going to need high-quality content to rank high in Google.
Google wants to deliver the very best search results to their users. If your content is not on that level, you’re going to struggle to get organic traffic.
I’ll tell you what I tell my clients and students: your leading focus for creating SEO content is to create the very best article on the topic, period.
Yes, user search intent is going to matter. Backlinks are going to matter, as well as all the other SEO ranking factors you have to deal with.
Still, your starting point is your own on-site SEO content. And for that, it’s all about creating the best online content you can provide.
Structuring Your Content For Search Engine Optimization
I’ll once again go back to this very article, this is exactly how you properly structure your content for SEO in 2022.
This specific article;
- Properly uses heading tags and keyword phrases within the headings
- Properly has unique sections that go into depth about the content matter being discussed
- Properly structured so users can quickly get to the content they care about the most
- Properly utilizes keywords throughout the article
While you can still rank content that is not structured like this article, it’s clear that Google prefers content that is structured just like this.
Gone are the days when you could rank terrible content.
Bad content does you no good anyway, you have to keep the end user in mind.
If you’re driving your target prospects and customers to bad content, are they more likely to purchase something from you? I highly doubt it.
Creating Awesome Content That Ranks On The 1st Page
Remember what I said about user search intent when you’re trying to figure out what content to create.
Each unique keywords is going to have different results, so you always want to match your content to exactly what that user is searching for.
Your goal should be to create the best content on the subject matter. Period.
Once you do your keyword research and determine what keywords you’re going to target, you can then build a content calendar to track all the content you’ll need to publish.
You can audit competitors to get an idea of what content to create, especially if that competitor ranks a lot of keywords on the 1st page of Google.
Furthermore, with E-E-A-T, you want to become an expert in your respected field – you want Google to view you as an expert.
If you’re creating great content, that will be a lot easier for you because people always want to share good content. This can help you business and brand gain attention and ultimately more backlinks (which are great for SEO).
